

- #Time complexity of enqueue and dequeue how to
- #Time complexity of enqueue and dequeue update
- #Time complexity of enqueue and dequeue code
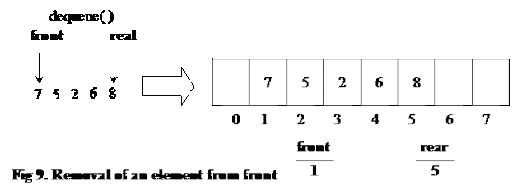
Let's learn how to remove Nodes from the Queue. But it doesn't have to be endless (but sometimes in hospitals and supermarkets it is so). If you look at the picture below it will be easier to understand the meaning. Time Complexity: O (1) for Enqueue (element insertion in the queue) as we simply increment pointer and put value in array and O (N) for Dequeue (element removing from the queue) as we use for loop to implement that. If you don't familiar with this methodology I highly recommend you to read the article about OOP on the freecodecamp web-page. We will use classes that are the main part of OOP (Object-oriented programming). And primarily we need to create the sample of the Node. Dequeue would be O (n) to move all elements a place back. Not the fact that using Insertion Sort, with O (n) complexity it would have suited my needs. If we continue our comparison, people in the queue are Nodes. It was very good for Dequeue (O (1)), and it had good enqueue complexity. It is just like a real queue of people in a supermarket.
#Time complexity of enqueue and dequeue code
Why do you need a Queue? What are the differences with Array?īefore we start to write the code let's discuss the main principle of the Queue Algorithm.There is no loop in any of the operations. Whoever you are, today we will discuss how to implement Queue Data Structure in JavaScript and what are its differences with a simple Array. Time Complexity: Time complexity of both operations enqueue () and dequeue () is O (1) as we only change few pointers in both operations. But if you are a programmer you associate it 99% with Data Structures and Algorithms. 2 (September 2003): 381–418.What do you imagine when you hear the word " Queue"? If you are not familiar with Programming you maybe think about the queue in shop or hospital. ‘Optimal Finger Search Trees in the Pointer Machine’.

: Brodal, Gerth Stølting, George Lagogiannis, Christos Makris, Athanasios Tsakalidis, and Kostas Tsichlas. This has O(1) get-min, extract-min, get-max, extract-max and O(log n) insert. count () : Gets count of total items in queue. peek () : Get the value of the front of the queue without removing it. dequeue (): Elements are removed from one end. enqueue (): Elements are added form one end (rear/back). More recently, a solution within Pointer-Machine model of computation has been given. Time and space complexity using LinkedList: Queue Operations: isEmpty (): Check if queue is empty or not. Our data structure uses the random-access machine (RAM) model with unit-cost measure and logarithmic word size Though this uses the RAM model of computation:
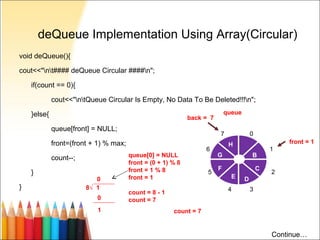
#Time complexity of enqueue and dequeue update
‘A Constant Update Time Finger Search Tree’. Linked List is a data structure consisting of a group of vertices (nodes) which together represent a sequence.
In Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on Algorithms and Data Structures, 282–290. īy using their data structure MAKEQUEUE, FINDMIN, DELETEMIN, DELETE can be supported in worst case time O(1), INSERT in worst case time O(log n) and MELD in worst case time O(n).īrodal, Gerth Stølting. IF MELD is allowed to take linear time it is possible to support DELETE-MIN in worst case constant time by using the finger search trees of Dietz and Raman. If you're willing to implement from the literature, then I have a much better solution for you.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
